Electrolyte Additives - 1,3 PS
From:VICKI Time:2021-04-01 11:24:11 Click:time
The oxidative decomposition of common lithium-ion battery electrolyte under high voltage limits the development of high-voltage lithium-ion batteries. In order to solve this problem, it is necessary to design and synthesize new high-pressure-resistant electrolytes or find suitable electrolyte additives. However, considering economic benefits, the development of appropriate electrolyte additives to stabilize the electrode/electrolyte is more favored by researchers.
Electrolyte additives for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries can be discussed in 6 parts, according to the types of additives, including boron-containing additives, organic phosphorus additives, carbonate additives, sulfur additives, ionic liquid additives, and other types of additives.
The following will focus on sulfur-containing additives (1,3-propane sultone), which is also our key product.
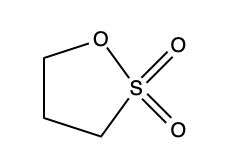
In recent years, there have been many reports on applying organic sulfonates as additives to lithium-ion batteries. PIRES adds 1,3-propane sultone (PS) to the electrolyte of high-voltage lithium-ion batteries, which effectively inhibits the occurrence of side reactions on the electrode surface and the dissolution of metal ions. ZHENG et al. used dimethylsulfonylmethane (DMSM) as a high-pressure LiNil/3Col/3Mn1/3O2 graphite battery electrolyte additive. XPS, SEM, and TEM analysis results show that the presence of MMDS has a good modification effect on the positive electrode SEI membrane. It can also significantly reduce the electrode/electrolyte interface impedance under high pressure and improve the positive electrode material's cycle stability. Also, HUANG et al. separately studied the cycle performance of trifluoromethyl phenyl sulfide (PTS) additives at room temperature and high temperature for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries. The analysis of theoretical calculation data and experimental results shows that the SEI film formed during the cycle improves the battery's cycle stability under high voltage.
In general, these two aspects limit the capacity and application of high-voltage cathode materials, including the continuous oxidative decomposition of the traditionally used organic carbonate electrolyte under high voltage and the transition metal dissolution ions of the cathode material.
The development of high-pressure electrolyte additives is an economical and effective way to improve battery performance. High-pressure additives generally oxidize preferentially than solvent molecules during the cycle, forming a passivation film on the positive electrode's surface, stabilizing the electrode/electrolyte interface, and finally realizing that the electrolyte can exist stably under high pressure.